Table of Contents
ToggleIn today’s fast-shifting global landscape, businesses can no longer rely on traditional methods, static processes, or outdated organizational structures. Markets move faster, customer expectations rise higher, and digital disruption reshapes industries at a pace many companies struggle to match. As a result, having a well-designed business transformation strategy has become an operational necessity—no longer a luxury reserved for global giants.
A successful business transformation strategy enables organizations to modernize their systems, improve internal performance, satisfy customers more effectively, adopt digital capabilities, and build resilience against economic volatility. From digital transformation and process re-engineering to leadership culture and customer experience redesign, this article explores the frameworks, methodologies, and best practices required to build a scalable, future-ready organization.
Below, we break down the essential components of a modern business transformation strategy, walking through critical pillars, common barriers, proven frameworks, and real-world examples.
What Is a Business Transformation Strategy? A Clear Explanation
A business transformation strategy is a structured, organization-wide plan to redesign processes, technologies, capabilities, and culture in order to improve long-term performance. It aligns leadership vision, operational priorities, digital initiatives, and workforce behaviors toward a shared future state.
Unlike short-term improvement projects, a business transformation strategy redefines how an organization functions at its core. It integrates digitalization, customer-centricity, process optimization, cultural evolution, and strategic growth planning into a cohesive roadmap.
Key purposes include:
Improving profitability
Enhancing customer value delivery
Increasing operational efficiency
Enabling digital maturity
Strengthening competitiveness
Preparing for future market shifts
The strength of a business transformation strategy lies in its ability to align every layer of the organization—people, processes, technology, and culture—toward a unified goal.
Why Business Transformation Matters Today
In 2026, nearly every industry is experiencing systemic change. Technological disruption, AI adoption, tighter regulatory requirements, global competition, sustainability pressures, and new consumer behaviors have created the need for strategic reinvention.
A strong business transformation strategy matters now more than ever because modern businesses face:
Digital acceleration driven by AI, automation, and smart data
Shifting customer expectations requiring personalization and faster service
Globalized supply chains vulnerable to disruptions
Economic volatility requiring agility and operational resilience
Sustainability mandates and ESG reporting requirements
Talent shortages requiring improved culture and capability building
Organizations that fail to implement a forward-thinking business transformation strategy risk losing market share, operational stability, and relevance.
Key Drivers of Business Transformation in Modern Organizations
The push toward a robust business transformation strategy typically arises from several internal or external forces:
1. Competitive Pressure
Competitors adopting AI, automation, and digital business models can threaten traditional players.
2. Revenue & Margin Decline
Business transformation helps restore profitability through leaner operations and new revenue streams.
3. Customer Experience Demands
Consumers expect seamless, fast, digital experiences across all touchpoints.
4. Operational Inefficiencies
Outdated processes create bottlenecks, waste, and rising operational costs.
5. Technology Obsolescence
Legacy systems limit innovation and scalability.
6. Regulatory & Compliance Needs
Industries must adapt to new data, privacy, finance, and sustainability regulations.
A well-designed business transformation strategy addresses all these drivers systematically.
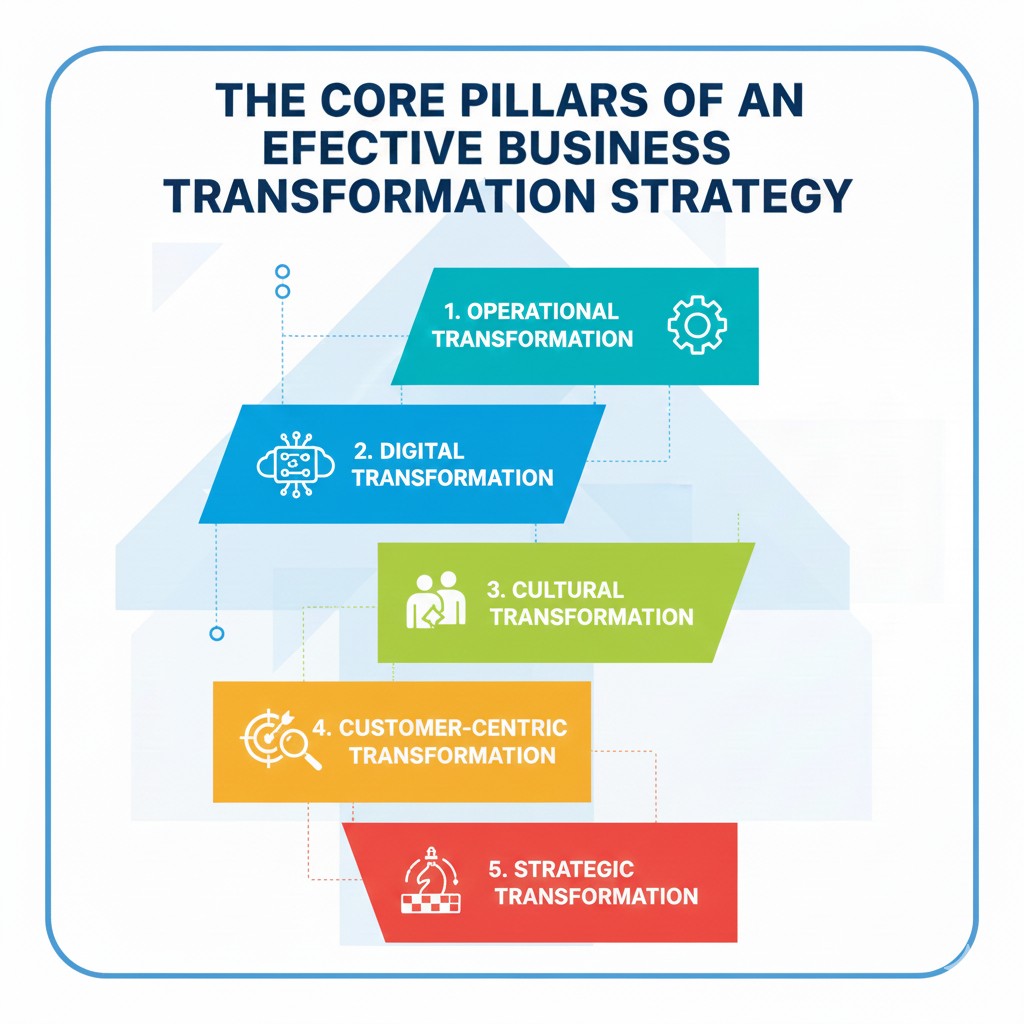
The Core Pillars of an Effective Business Transformation Strategy
A complete business transformation strategy is built on five essential pillars:
1. Operational Transformation
Improving day-to-day processes, workflows, and performance metrics.
Focus areas include:
Lean process design
Workflow automation
Cost optimization
Standardized operations
Quality improvement
2. Digital Transformation
Integrating modern technologies to increase efficiency and create value.
This includes:
ERP modernization
Data analytics
AI and automation
Cloud technologies
Cybersecurity
IoT and smart infrastructure
3. Cultural Transformation
Building a workforce mindset aligned with innovation, accountability, and collaboration.
Characteristics include:
Strong leadership behaviors
Employee engagement
Continuous learning
Clear communication
4. Customer-Centric Transformation
Rebuilding products, services, and experiences around customer needs.
Focus areas:
Customer journey redesign
Personalization
Faster service fulfillment
Customer feedback loops
5. Strategic Transformation
Redefining business models, market positions, and long-term vision.
This pillar involves:
New revenue streams
Partnerships and ecosystems
Global expansion
Sustainability integration
When these pillars reinforce each other, the business transformation strategy becomes a powerful blueprint for long-lasting success.
Operational Transformation: Streamlining Processes for Efficiency
Companies often begin their business transformation strategy with operational improvements, because inefficiencies directly impact costs, productivity, and customer satisfaction.
Typical initiatives include:
Process mapping and re-engineering
Lean Six Sigma deployment
Automation of repetitive tasks
Centralized data and workflow systems
Improved cross-department communication
A strong business transformation strategy reduces waste, increases process speed, and strengthens the foundation for digital adoption.
Digital Transformation: Technology, Automation & Data Integration
Digital maturity is now a competitive differentiator. A modern business transformation strategy must fully integrate digital tools that enhance speed, accuracy, and decision-making.
Digital transformation includes:
Modern ERP platforms (SAP, Oracle, D365)
AI-driven forecasting and analytics
Robotics and automation
Cybersecurity frameworks
Smart infrastructure (IoT sensors, digital twins)
Technology adoption without strategy leads to fragmentation—this is why a business transformation strategy ensures alignment across systems, data, and workflows.
Cultural Transformation: Aligning People, Behaviors & Leadership
Transformation fails if culture resists change. A successful business transformation strategy includes structured cultural initiatives such as:
Leadership development
Transparent communication
Employee training and upskilling
Incentives aligned with transformation goals
Cross-functional collaboration
Culture is where strategy becomes reality.
Customer-Centric Transformation: Rebuilding Value Delivery Models
Customer expectations evolve faster than internal processes. A strong business transformation strategy ensures companies redesign experiences around customer needs.
Top initiatives include:
Customer journey optimization
Real-time service visibility
Personalization through data
Faster, omnichannel communication
This ensures customer satisfaction increases alongside operational efficiency.
Common Challenges Companies Face During Transformation
Even the best business transformation strategy faces obstacles, including:
Resistance to change
Lack of leadership alignment
Budget constraints
Legacy systems and data fragmentation
Skill gaps
Poor project governance
Misaligned KPIs
Addressing these barriers early ensures smoother transformation execution.
Business Transformation Frameworks: Proven Models You Can Use
Several respected frameworks strengthen a business transformation strategy, including:
McKinsey 7S Model
Kotter’s 8-Step Change Model
ADKAR Change Management
Business Model Canvas
SCOR Model for operations
Lean and Six Sigma
Balanced Scorecard
Using frameworks ensures strategic clarity and structured implementation.
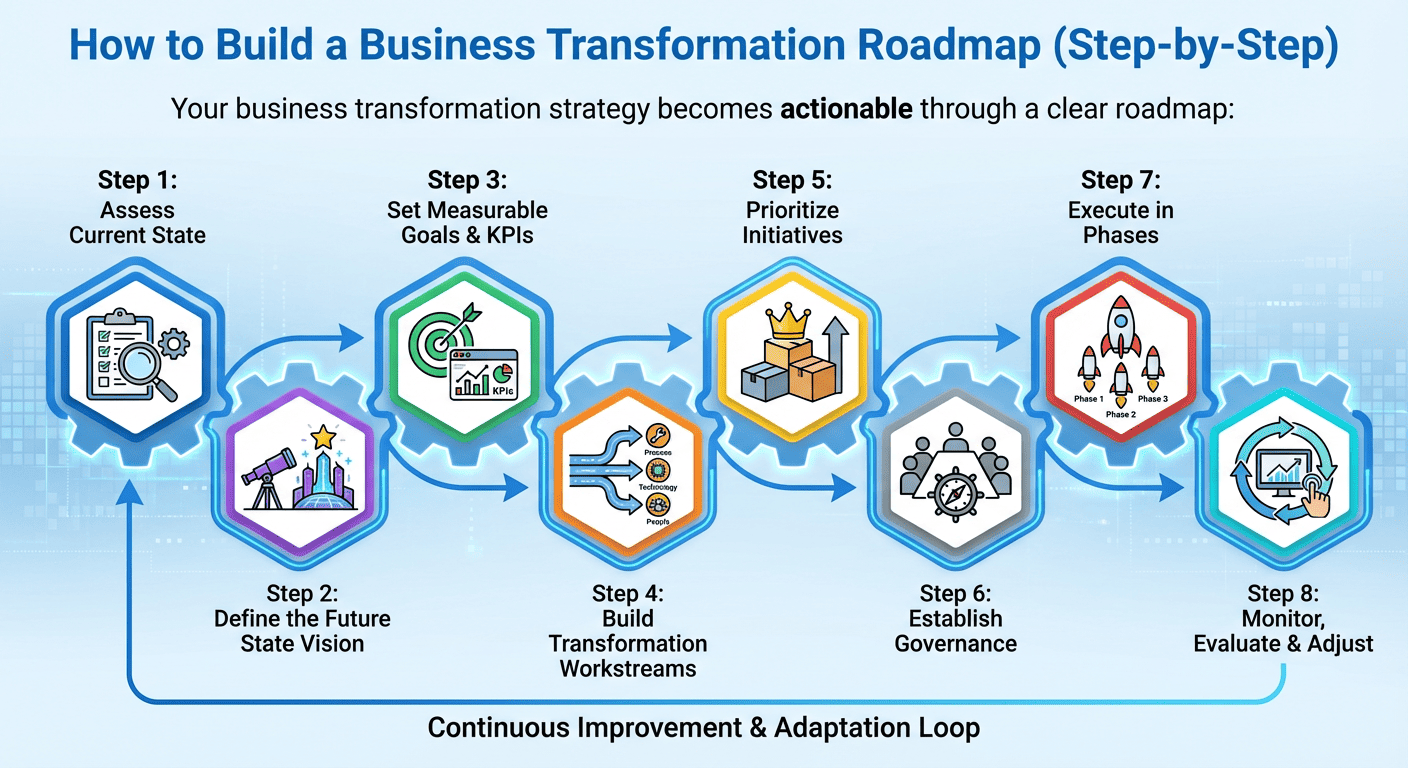
How to Build a Business Transformation Roadmap (Step-by-Step)
Your business transformation strategy becomes actionable through a clear roadmap:
Step 1: Assess Current State
Identify gaps in processes, technology, culture, and customer experience.
Step 2: Define the Future State Vision
Clarify where the organization needs to be in 3–5 years.
Step 3: Set Measurable Goals & KPIs
Align goals to strategic priorities and performance metrics.
Step 4: Build Transformation Workstreams
Organize initiatives into digital, operational, cultural, and customer-centric streams.
Step 5: Prioritize Initiatives
Focus on high-impact, high-feasibility projects.
Step 6: Establish Governance
Create steering committees, PMOs, and reporting systems.
Step 7: Execute in Phases
Deploy iterative improvements, not one massive change.
Step 8: Monitor, Evaluate & Adjust
A business transformation strategy is a living system that evolves as the organization grows.
KPIs and Metrics to Measure Transformation Success
Measuring success is vital for validating your business transformation strategy. Key metrics include:
Operating cost reductions
Revenue growth
Digital adoption rates
Customer satisfaction (NPS)
Employee engagement
Time-to-delivery improvements
Error rate reductions
Automation ROI
Dashboards and analytics help track progress transparently.
Role of Consultants in the Transformation Journey
Sometimes, external expertise is required to design or accelerate a business transformation strategy.
Consultants bring:
Neutral perspective
Global best practices
Proven methodologies
Specialized digital skills
Change management expertise
They are especially valuable for large transformations or organizations with limited internal capability.
Real-World Examples of Successful Business Transformation
1. Retail Transformation
Brick-and-mortar stores implemented omnichannel systems, AI inventory optimization, and customer personalization—with dramatic improvements in sales and loyalty.
2. Manufacturing Transformation
Factories deploying IoT sensors, predictive maintenance, and digital twins saw productivity surge and downtime drop.
3. Financial Services Transformation
Banks adopting automation, digital onboarding, and mobile-first models improved compliance and customer experience.
In all these cases, a committed business transformation strategy was the backbone of success.
Future Trends Shaping Business Transformation
Looking ahead, several trends will influence every business transformation strategy:
Autonomous operations
AI-driven decision systems
Sustainability and circular economy models
Hyper-automation
Global digital workforce
Cloud-native infrastructure
Real-time customer personalization
Future transformation will be continuous—not event-based.
Final Thoughts
Business transformation is not a project — it is a long-term discipline. Companies that thrive in the coming decade will be those that understand how to balance strategic vision with operational execution, cultural change, and technological innovation. A strong transformation strategy empowers organizations to reinvent themselves, unlock new value, and build long-term resilience.
Transformation requires courage, leadership, and commitment — but the rewards are substantial: competitiveness, efficiency, customer loyalty, and sustainable growth.
F.A.Qs
Frequently asked questions
To redesign the organization for future competitiveness by improving processes, technology, customer experience, and culture.
Anywhere from 12 to 36 months depending on complexity, scope, and internal readiness.
Employee resistance and poor change management are the most common causes of failure.
No. Digital transformation focuses on technology; business transformation includes operations, culture, customer experience, and strategy.
Not always — but consultants accelerate progress, reduce risk, and bring proven methodologies.
Other Questions
General questions
Leaders set vision, allocate resources, and inspire employees. Without leadership, initiatives fail.
KPIs include revenue growth, market share, customer satisfaction, and innovation rate.
Banking, healthcare, retail, logistics, and manufacturing.
Kodak and Nokia are classic examples of missed transformation opportunities.
AI, sustainability, and global collaboration will shape the next era of transformation.








No comment